他身在高楼广厦之中,却有山泽鱼鸟之思
1088 字
5 分钟
gromacs图片绘制
前言
TIP准备工作 gmx的运行结果
tpr,xtc
直接运行下述ipynb脚本,进行结果分析
import subprocess
import os
# Function to run shell commands
def run_command(command, input_data=None):
process = subprocess.Popen(command, shell=True, stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
stdout, stderr = process.communicate(input=input_data)
if process.returncode != 0:
print(f"Error: {stderr}")
else:
print(stdout)
# Activate the conda environment (note: this might not work as expected in Jupyter Notebook)
# It's better to activate the environment outside Jupyter Notebook before running the notebook
# run_command("conda activate gmxMMPBSA")
# Create directory and extract files
#run_command("mkdir -p 422gmc_output")
#run_command("tar -xzvf 422gmc_output.tar.gz -C 422gmc_output")
# Change to the desired directory
os.chdir("/home/starparyer/task/ding0617md/422/422gmc_output/gromacs")
# RMSD
run_command("echo '1 1' | gmx rms -s step5_1.tpr -f step5_1.xtc -o rmsd.xvg -tu ns")
# RMSF
run_command("echo '0' | gmx rmsf -s step5_1.tpr -f step5_1.xtc -n index.ndx -o rmsf.xvg -ox avg.pdb -res -oq bfac.pdb")
# H-bond
run_command("echo '1\n13' | gmx hbond -f step5_1.xtc -s step5_1.tpr -num hbond_num.xvg")
# Solvent Accessible Surface Area (SASA)
run_command("echo '1' | gmx sasa -s step5_1.tpr -f step5_1.xtc -o sasa.xvg")
# Radius of gyration (Rg)
run_command("echo '1' | gmx gyrate -s step5_1.tpr -f step5_1.xtc -o rg.xvg")
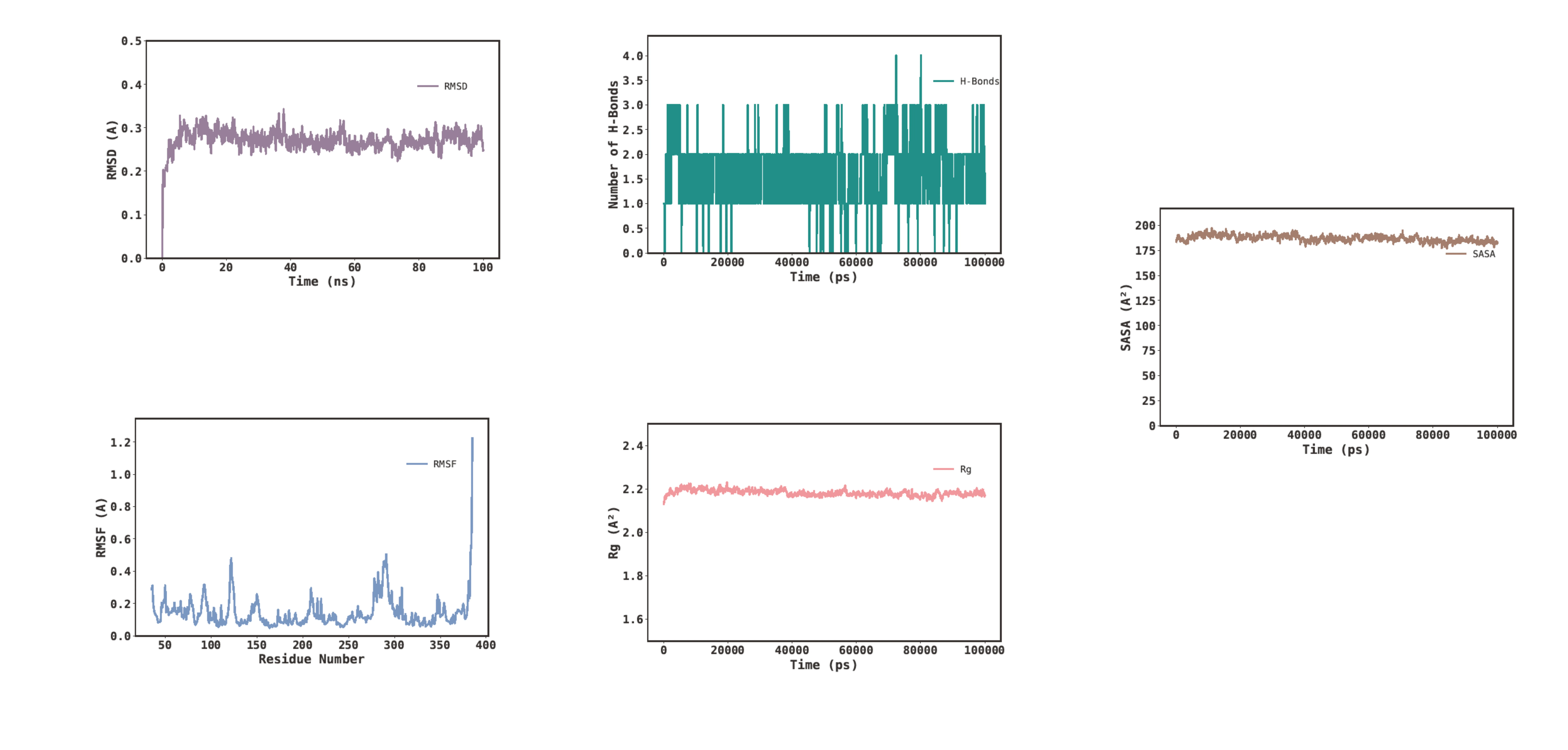
RMSD
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# 读取 xvg 文件,跳过任何注释行
def read_xvg(filename):
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
data = []
for line in file:
if not line.startswith(('#', '@')):
data.append(line.strip().split())
return pd.DataFrame(data, columns=["time", "rmsd"]).astype(float)
# 读取 RMSD 数据
df = read_xvg("rmsd.xvg")
# 提取时间和 RMSD 列
time = df["time"]
rmsd = df["rmsd"]
# 绘制图形
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.25, right=0.9, top=0.9, bottom=0.3)
ax = plt.gca()
# 折线的粗细
line_width = 2.5
plt.plot(time, rmsd, linewidth=line_width, label="RMSD", color="#957A98", alpha=1.0)
# 设置标签的字体大小
xlabel_fontsize = 20
ylabel_fontsize = 20
xtick_fontsize = 18
ytick_fontsize = 18
legend_fontsize = 15
plt.xlabel('Time (ns)', fontname="monospace", fontsize=xlabel_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.ylabel('RMSD (A)', fontname="monospace", fontsize=ylabel_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.xticks(fontname="monospace", rotation=0, size=xtick_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.yticks(fontname="monospace", size=ytick_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.ylim(0, 0.5) # 根据你的数据范围调整 ylim
# 图例的位置和大小
legend_loc = (0.76, 0.75)
plt.legend(loc=legend_loc, ncol=1, frameon=False, prop={"family": "monospace", "size": legend_fontsize})
# 修改坐标轴线的粗细
axis_linewidth = 2.0
ax.spines['top'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['left'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['right'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
plt.show()
fig.savefig('rmsd_plot.pdf')
RMSD
RMSF
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# 读取 xvg 文件,跳过任何注释行
def read_xvg(filename):
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
data = []
for line in file:
if not line.startswith(('#', '@')):
data.append(line.strip().split())
return pd.DataFrame(data, columns=["residue", "rmsf"]).astype(float)
# 读取 RMSF 数据
df = read_xvg("rmsf.xvg")
# 提取残基编号和 RMSF 列
residue_numbers = df["residue"]
rmsf_values = df["rmsf"]
# 绘制图形
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.25, right=0.9, top=0.9, bottom=0.3)
ax = plt.gca()
# 折线的粗细
line_width = 2.5
plt.plot(residue_numbers, rmsf_values, linewidth=line_width, label="RMSF", color="#7794C1", alpha=1.0)
# 设置标签的字体大小
xlabel_fontsize = 20
ylabel_fontsize = 20
xtick_fontsize = 18
ytick_fontsize = 18
legend_fontsize = 15
plt.xlabel('Residue Number', fontname="monospace", fontsize=xlabel_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.ylabel('RMSF (A)', fontname="monospace", fontsize=ylabel_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.xticks(fontname="monospace", rotation=0, size=xtick_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.yticks(fontname="monospace", size=ytick_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.ylim(0, max(rmsf_values) * 1.1) # 根据数据范围调整 ylim
# 图例的位置和大小
legend_loc = (0.76, 0.75)
plt.legend(loc=legend_loc, ncol=1, frameon=False, prop={"family": "monospace", "size": legend_fontsize})
# 修改坐标轴线的粗细
axis_linewidth = 2.0
ax.spines['top'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['left'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['right'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
plt.show()
# 保存绘图为 PDF
fig.savefig('rmsf_plot.pdf')
H-BOND
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# 读取 xvg 文件,跳过任何注释行
def read_xvg(filename):
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
data = []
for line in file:
if not line.startswith(('#', '@')):
data.append(line.strip().split())
return pd.DataFrame(data, columns=["time", "hbond_count"]).astype(float)
# 读取氢键数据
df = read_xvg("hbond_num.xvg")
# 提取时间和氢键数量列
time = df["time"]
hbond_count = df["hbond_count"]
# 绘制图形
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.25, right=0.9, top=0.9, bottom=0.3)
ax = plt.gca()
# 折线的粗细
line_width = 2.5
plt.plot(time, hbond_count, linewidth=line_width, label="H-Bonds", color="#008b84", alpha=1.0)
# 设置标签的字体大小
xlabel_fontsize = 20
ylabel_fontsize = 20
xtick_fontsize = 18
ytick_fontsize = 18
legend_fontsize = 15
plt.xlabel('Time (ps)', fontname="monospace", fontsize=xlabel_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.ylabel('Number of H-Bonds', fontname="monospace", fontsize=ylabel_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.xticks(fontname="monospace", rotation=0, size=xtick_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.yticks(fontname="monospace", size=ytick_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.ylim(0, max(hbond_count) * 1.1) # 根据数据范围调整 ylim
# 图例的位置和大小
legend_loc = (0.8, 0.75)
plt.legend(loc=legend_loc, ncol=1, frameon=False, prop={"family": "monospace", "size": legend_fontsize})
# 修改坐标轴线的粗细
axis_linewidth = 2.0
ax.spines['top'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['left'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['right'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
plt.show()
# 保存绘图为 PDF
fig.savefig('hbond_plot.pdf')
SASA
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
def read_xvg(filename):
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
data = []
for line in file:
if not line.startswith(('#', '@')):
data.append(line.strip().split())
return pd.DataFrame(data, columns=["time", "sasa"]).astype(float)
# 读取SASA数据
df = read_xvg("sasa.xvg")
time = df["time"]
sasa = df["sasa"]
# 绘制图形
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.25, right=0.9, top=0.9, bottom=0.3)
ax = plt.gca()
# 可选参数设置
line_width = 2.5
xlabel_fontsize = 20
ylabel_fontsize = 20
xtick_fontsize = 18
ytick_fontsize = 18
legend_fontsize = 15
axis_linewidth = 2.0
legend_loc = (0.8, 0.75)
plt.plot(time, sasa, linewidth=line_width, label="SASA", color="#a17a68", alpha=1.0)
plt.xlabel('Time (ps)', fontname="monospace", fontsize=xlabel_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.ylabel('SASA (A²)', fontname="monospace", fontsize=ylabel_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.xticks(fontname="monospace", rotation=0, size=xtick_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.yticks(fontname="monospace", size=ytick_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.ylim(0, max(sasa) * 1.1)
plt.legend(loc=legend_loc, ncol=1, frameon=False, prop={"family": "monospace", "size": legend_fontsize})
ax.spines['top'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['left'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['right'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
plt.show()
fig.savefig('sasa_plot.pdf')
RG
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
def read_xvg(filename):
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
data = []
for line in file:
if not line.startswith(('#', '@')):
data.append(line.strip().split())
# 假定文件中有五列数据
return pd.DataFrame(data, columns=["time", "Rg", "Rg_sX_N", "Rg_sY_N", "Rg_sZ_N"]).astype(float)
# 读取Rg数据
df = read_xvg("rg.xvg")
time = df["time"]
rg = df["Rg"]
# 绘图代码保持不变
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.25, right=0.9, top=0.9, bottom=0.3)
ax = plt.gca()
# 可选参数设置
line_width = 2.5
xlabel_fontsize = 20
ylabel_fontsize = 20
xtick_fontsize = 18
ytick_fontsize = 18
legend_fontsize = 15
axis_linewidth = 2.0
legend_loc = (0.8, 0.75)
plt.plot(time, rg, linewidth=line_width, label="Rg", color="#f29398", alpha=1.0)
plt.xlabel('Time (ps)', fontname="monospace", fontsize=xlabel_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.ylabel('Rg (A²)', fontname="monospace", fontsize=ylabel_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.xticks(fontname="monospace", rotation=0, size=xtick_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.yticks(fontname="monospace", size=ytick_fontsize, weight="bold")
plt.ylim(1.5, 2.5)
plt.legend(loc=legend_loc, ncol=1, frameon=False, prop={"family": "monospace", "size": legend_fontsize})
ax.spines['top'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['left'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
ax.spines['right'].set_linewidth(axis_linewidth)
plt.show()
fig.savefig('rg_plot.pdf')
图片参考